Where Do I Upload My Expansion Apk .obb File
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical back up.
APK Expansion Files
Some applications (some games, for instance) require more resources and assets than can be provided in the maximum Android app size limit imposed by Google Play. This limit depends on the version of Android that your APK is targeted for:
- 100MB for APKs that target Android 4.0 or higher (API level xiv or higher).
- 50MB for APKs that target Android 3.2 or lower (API level 13 or higher).
To overcome this limitation, Google Play will host and distribute two expansion files to continue with an APK, assuasive an application to indirectly exceed this limit.
On most devices, when an awarding is installed, expansion files will be downloaded along with the APK and will be saved to the shared storage location (the SD card or the USB-mountable partition) on the device. On a few older devices, the expansion files may non automatically install with the APK. In these situations, information technology is necessary for the application to contain lawmaking that will download the expansion files when the user showtime runs the applications.
Expansion files are treated as opaque binary blobs (obb) and may be upward to 2GB in size. Android does not perform any special processing on these files afterwards they are downloaded – the files can be in whatsoever format that is appropriate for the awarding. Conceptually, the recommended arroyo to expansion files is as follows:
- Main expansion – This file is the primary expansion file for resources and avails that will not fit in the APK size limit. The master expansion file should contain the primary avails that an application needs and should rarely exist updated.
- Patch expansion – This is intended for small updates to the primary expansion file. This file tin can be updated. It is the responsibility of the awarding to perform any necessary patches or updates from this file.
The expansion files must be uploaded at the aforementioned time equally the APK is uploaded. Google play does non allow an expansion file to be uploaded to an existing APK or for existing APKs to exist updated. If it is necessary to update an expansion file, so a new APK must be uploaded with the versionCode updated.
Expansion File Storage
When the files are downloaded to a device, they will be stored in shared-store/Android/obb/package-proper noun :
- shared-store – This is the directory specified by
Android.Os.Environment.ExternalStorageDirectory. - packet-proper name – This is the application's Java-way packet name.
In one case downloaded, expansion files should non be moved, altered, renamed, or deleted from their location on the device. To exercise and so will crusade the expansion files to be downloaded once again, and the old file(southward) will be deleted. Additionally, the expansion file directory should comprise merely the expansion pack files.
Expansion files offering no security or protection around their content – other applications or users may access whatever files saved on the shared storage.
If information technology is necessary to unpack an expansion file, the unpacked files should be stored in a separate directory, such as one in Android.OS.Surround.ExternalStorageDirectory.
An alternative to extracting files from an expansion file is to read the assets or resource directly from the expansion file. The expansion file is nothing more than than a cipher file that can be used with an advisable ContentProvider. The Android.Play.ExpansionLibrary contains an associates, System.IO.Pinch.Null, which includes a ContentProvider that will allow for directly file access to some media files. If media files are being packaged into a nada file, media playback calls may direct use files in the goose egg without having to unpack the zip file. The media files should non be compressed when added to the zip file.
FileName Format
When the expansion files are downloaded, Google Play will apply the post-obit scheme to name the expansion:
[main|patch].<expansion-version>.<package-name>.obb The three components of this scheme are:
-
primaryorpatch– This specifies whether this is the main or patch expansion file. There can be just one of each. -
<expansion-version>– This is an integer that matches theversionCodeof the APK that the file was first associated with. -
<package-proper noun>– This is the awarding'southward Java-style packet proper name.
For example, if the APK version is 21, and the package proper name is mono.samples.helloworld, the main expansion file will be named main.21.mono.samples.helloworld.
Download Process
When an application is installed from Google Play, the expansion files should be downloaded and saved along with the APK. In certain situations this may not happen, or expansion files may exist deleted. To handle this condition, an app needs to check to run across whether the expansion files be and so download them, if necessary. The following flowchart displays the recommended workflow of this process:
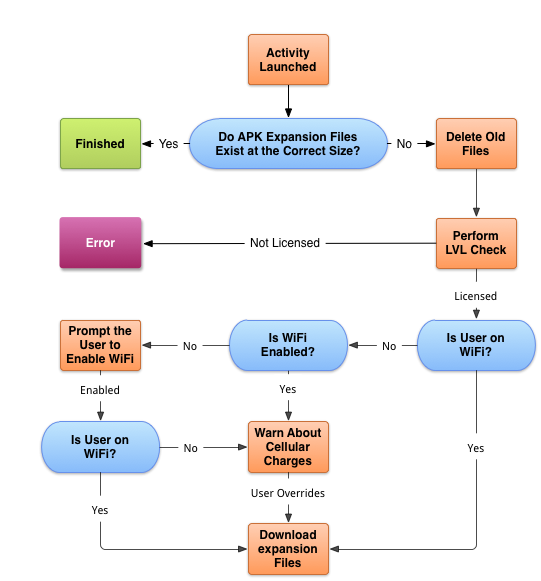
When an application starts up, it should check to see if the appropriate expansion files exist on the electric current device. If they practice not, then the awarding must brand a request from Google Play's Application Licensing. This bank check is made past using the License Verification Library (LVL), and must be made for both gratis and licensed applications. The LVL is primarily used by paid applications to enforce license restrictions. Still, Google has extended the LVL and so that information technology tin can be used with expansion libraries equally well. Free applications take to perform the LVL check, but tin ignore the license restrictions. The LVL request is responsible for providing the following information about the expansion files that the application requires:
- File Size – The file sizes of the expansion files are used equally part of the bank check that determines whether or not the correct expansion files have already been downloaded.
- Filenames – This is the file name (on the electric current device) to which the expansion packs must be saved.
- URL for Download – The URL that should be used to download the expansion packs. This is unique for every download and will expire before long after it is provided.
Subsequently the LVL cheque has been performed, the awarding should download the expansion files, taking into consideration the following points as role of the download:
- The device may not accept enough space to store the expansion files.
- If Wi-Fi is not available, then the user should be immune to break or abolish the download to prevent unwanted information charges.
- The expansion files are downloaded in the background to avoid blocking user interactions.
- While the download is occurring in the background, a progress indicator should be displayed.
- Errors that occur during the download are gracefully handled and recoverable.
Architectural Overview
When the main activeness starts, it checks to come across if the expansion files are downloaded. If the files are downloaded, they must be checked for validity.
If the expansion files have non been downloaded or if the current files are invalid, so new expansion files must be downloaded. A divisional service is created as function of the application. When the main activeness of the application is started, it uses the bounded service to perform a check against the Google Licensing services to find out the expansion file names and the URL of the files to download. The bounded service will then download the files on a background thread.
To ease the effort required to integrate expansion files into an awarding, Google created several libraries in Java. The libraries in question are:
- Downloader Library – This is a library that reduces the endeavour required to integrate expansion files in an application. The library will download the expansion files in a background service, display user notifications, handle network connectivity problems, resume downloads, etc.
- License Verification Library (LVL) – A library for making and processing the calls to the Application Licensing services. Information technology can also be used to perform licensing checks, to run into if the application is authorized for utilise on the device.
- APK Expansion Naught Library (optional) – If the expansion files are in a nothing file, this library will act as a content provider and permit an application to read resources and assets directly from the zero file without having to aggrandize the zip file.
These libraries have been ported to C# and are bachelor under the Apache 2.0 license. To quickly integrate expansion files into an existing application, these libraries can be added to an existing Xamarin.Android awarding. The code is available at the Android.Play.ExpansionLibrary on GitHub.
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/android/deploy-test/publishing/publishing-to-google-play/apk-expansion-files
Posted by: rodriguezrawastrand.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Where Do I Upload My Expansion Apk .obb File"
Post a Comment